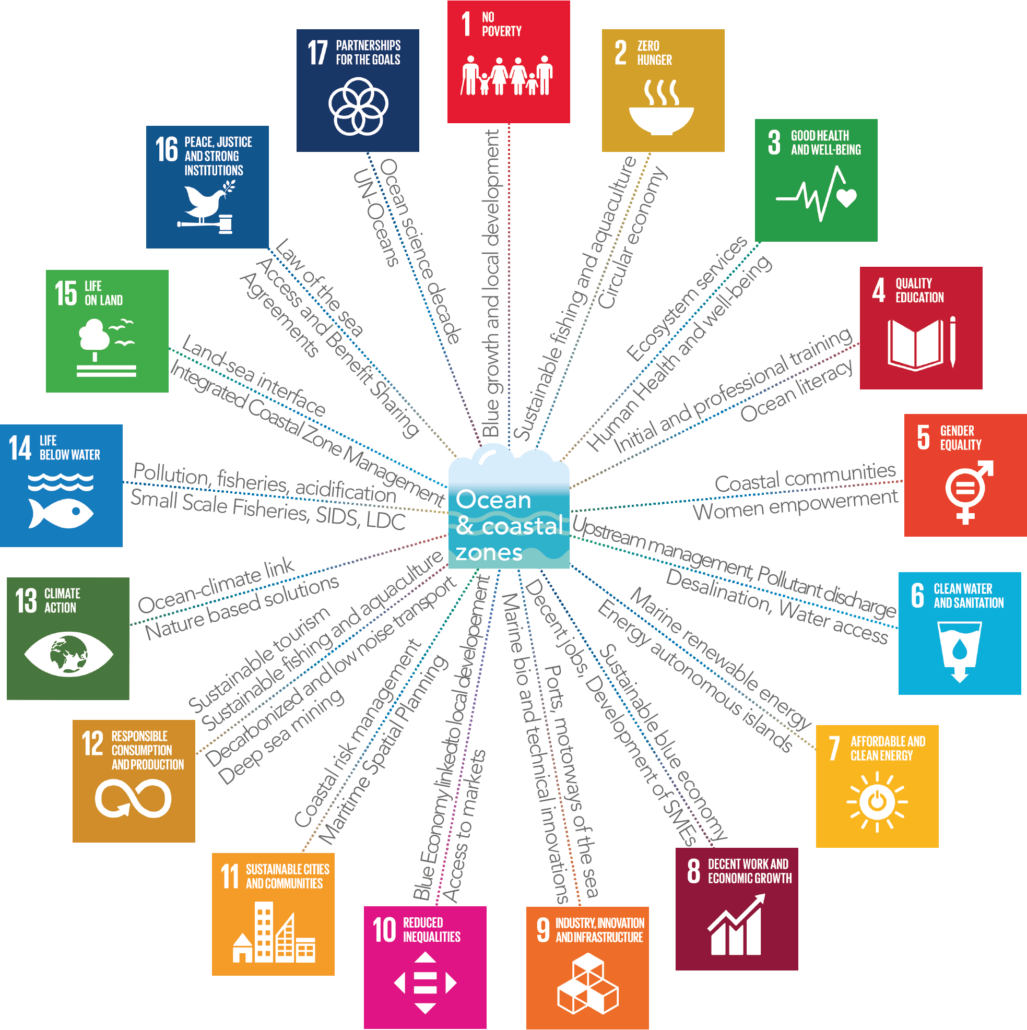
Blue growht and local development
Sustainable fishing and aquaculture ; Circular economy
Ecosystem services ; Human Health and well-being
Initial and professional training ; Ocean literacy
Coastal communities ; Women empowerment
Upstream management, Pollutant discharge ; Desalination, Water access
Marine renewable energy ; Energy autonomous islands
Sustainable blue economy ; Decent jobs, Development of Small and Medium Size Entreprises (SMEs)
Ports, motorways of the sea ; Marine bio and technical innovations
Blue Economy linked to local developement ; Access to markets
Coastal risk management ; Maritime Spatial Planning
Sustainable tourism, Sustainable fishing and aquaculture ; Decarbonized and low noise transport, Deep sea mining
Ocean-climate link ; Nature based solutions
Pollution, fisheries, acidification ; Small Scale Fisheries, Small Island Developing States (SIDS), Least Developed Countries (LDC)
Land-sea interface ; Integrated Coastal Zone Management
Law of the sea ; Access Benefit Sharing Agreements
Ocean science decade ; UN-Oceans
Ocean & coastal zones
The importance of the ocean for sustainable development has been firmly recognized in the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. Goal 14 specifically addresses the need for sustainable use and conservation of marine and coastal ecosystems. It sets targets to manage and combat the adverse effects of overfishing, growing ocean acidification and pollution of all kinds. It also calls for the expansion of the scope of MPAs for the protection of marine biodiversity. In the sustainable use of marine resources, it emphasizes the importance of the ocean for Small Island Developing States and access to resources and markets for small fisheries. ODD 14 calls for “an intensification of research capacity and increase in ocean sciences funding” to preserve marine resources and the ocean ecosystem.
But the ocean and coastal areas are more than that. Covering three quarters of the Earth’s surface, the ocean contains more than 90 percent of our planet’s living species, provide food for billions of people, supports more than 90 percent of all world trade through maritime transport, and is a growing source of renewable energy as much as it is a minerals reserve. An ever-growing proportion of the world’s population lives near the ocean and many communities depend on access to those resources. The ocean and coastal zones are crucial to human well-being. Exposed to the consequences of increasing anthropogenic pressures and global change, they deserve particular attention. The SDGs give a unified vision for both their protection and their enhancement.
See this page in: Français







 OUI
OUI